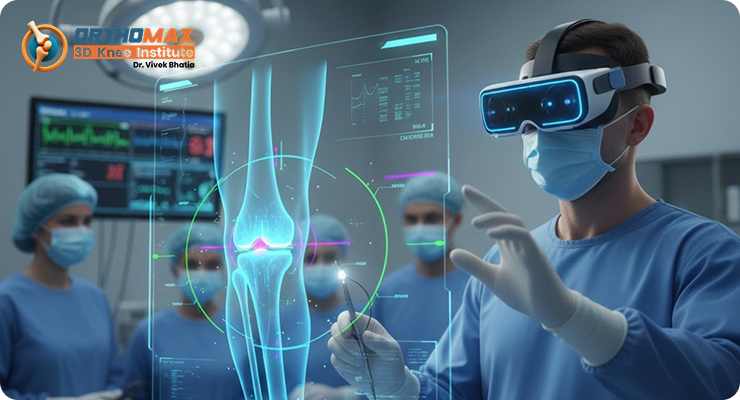
How Augmented Reality Is Transforming Modern Knee Replacement
Knee pain is no longer an “old-age problem.” From athletes to working professionals and seniors, knee joint degeneration and injuries affect daily life across age groups. As expectations from surgery grow—less pain, faster recovery, and longer implant life—technology has stepped in to reshape outcomes. One of the most impactful innovations today is Augmented Reality (AR) in orthopaedic surgery. Augmented Reality is changing how surgeons plan, perform, and perfect knee replacement procedures. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on experience and estimation, AR enables real-time visual guidance, precision alignment, and patient-specific customization. This shift is especially visible in advanced orthopaedic centers and among the best orthopaedics in Panchkula, where technology-driven care is redefining standards. What Is Augmented Reality in Knee Replacement? Augmented Reality blends digital information with the surgeon’s real-world view during surgery. Using smart glasses, navigation systems, or digital overlays, AR projects 3D anatomical data directly onto the patient’s knee during the operation. In simple terms: This approach is increasingly used in modern knee replacement surgeries to improve consistency and long-term success. Why Precision Matters in Knee Replacement Even a small error of 1–2 degrees in implant placement can: Traditional techniques depend largely on manual tools and the surgeon’s experience. AR introduces objective precision, ensuring every step aligns with the patient’s anatomy. That’s why AR based knee replacement is seen as a breakthrough rather than just a technological upgrade. How AR Transforms the Knee Replacement Process 1. Advanced Pre-Surgical Planning Before surgery, CT scans or 3D imaging are used to: This personalized planning improves predictability and minimizes surprises during surgery. 2. Real-Time Surgical Guidance During surgery, AR systems: This allows instant correction, making surgery more accurate and controlled. 3. Minimal Invasive Accuracy Because AR reduces uncertainty: These advantages directly contribute to faster recovery and better outcomes. Benefits of AR Based Knee Replacement for Patients Patients choosing AR based knee replacement often experience measurable advantages: Leading specialists among the best orthopaedics in Panchkula now recommend AR-assisted procedures for suitable candidates seeking long-term results. AR vs Traditional Knee Replacement: A Clear Shift Aspect Traditional Surgery AR-Based Surgery Implant alignment Manual estimation Real-time guided Precision level Surgeon-dependent Technology-assisted Recovery consistency Variable More predictable Long-term results Good Superior and durable While traditional knee replacement is still effective, AR adds a layer of accuracy that significantly improves surgical outcomes. Is Augmented Reality Safe and Reliable? Yes. AR in orthopaedics is: Experienced orthopaedic surgeons use AR as an enhancement—combining skill with technology for better patient safety. Who Is an Ideal Candidate for AR Knee Replacement? You may benefit from AR-assisted knee surgery if: Consultation with experts from the best orthopaedics in Panchkula helps determine suitability based on lifestyle, age, and joint condition. Recovery Experience with AR Based Knee Replacement Patients often report: Because the joint mechanics are restored more accurately, physiotherapy becomes smoother and more effective. Role of Surgeon Expertise with AR Technology Technology alone does not guarantee success. Outcomes depend on: That’s why choosing specialists trained in AR based knee replacement is critical. Reputed centers offering advanced knee replacement procedures focus equally on skill and innovation. Why This Matters for Patients in Panchkula With growing access to advanced orthopaedic care, patients no longer need to travel far for world-class treatment. Many clinics led by the best orthopaedics in Panchkula now offer technology-driven solutions comparable to global standards. This makes Panchkula an emerging hub for advanced joint replacement care in North India. FAQs Q1. Is AR-based knee replacement better than robotic surgery? AR focuses on visual guidance and precision, while robotics assist with mechanical execution. Both are effective, and choice depends on surgeon expertise and patient needs. Q2. Does AR-based surgery increase operation time? No. In most cases, planning reduces intraoperative time by improving workflow efficiency. Q3. Is AR knee replacement costlier? Costs may be slightly higher, but reduced complications and long-term benefits often make it cost-effective. Q4. Is recovery faster with AR knee replacement? Yes. Improved alignment leads to quicker mobility and smoother rehabilitation. Q5. Can elderly patients undergo AR-based knee replacement? Yes, age is not a limitation. Overall health and joint condition matter more. Final Thoughts Augmented Reality is not the future of orthopaedics—it’s the present. By combining surgical expertise with digital precision, AR is transforming how knee replacement surgeries are performed and experienced. For patients seeking accuracy, faster recovery, and lasting results, AR based knee replacement offers a smarter, safer path forward. With access to skilled surgeons and advanced care from the Orthomax’s best orthopaedics in Panchkula, patients can confidently step into a pain-free, active life.