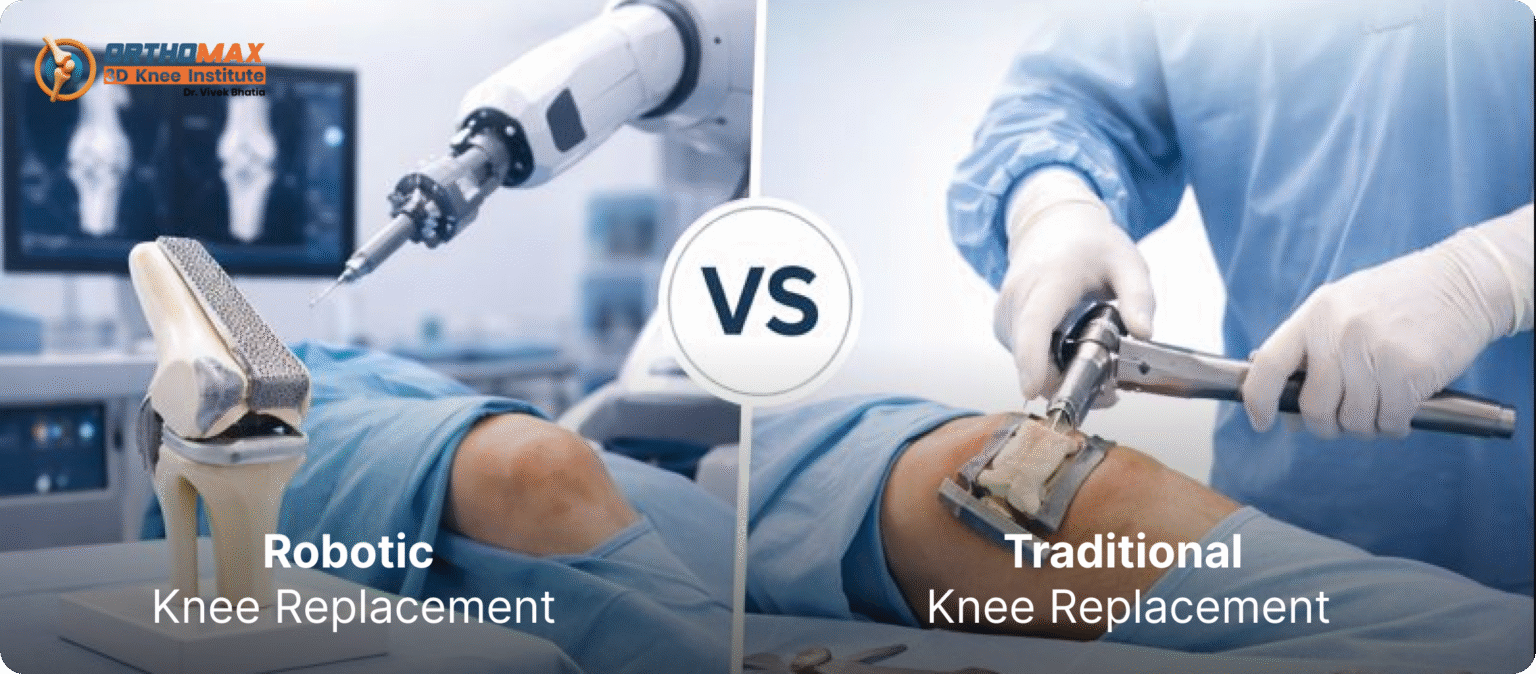
Robotic vs Traditional Knee Replacement: Key Differences Explained
Knee replacement surgery has helped millions of people regain mobility, reduce pain, and return to the activities they love. Yet, as medical technology continues to advance, patients today have more options than ever. Two of the most widely discussed approaches are traditional knee replacement and robotic knee replacement. While both aim to restore function and relieve joint pain caused by arthritis or injury, each method differs in precision, technique, recovery, and long-term outcomes.
If you are considering knee surgery—either now or in the future—understanding the differences between robotic and traditional approaches can help you make a confident and informed decision. This complete comparison breaks down how each works, their benefits and limitations, cost factors, patient experiences, recovery expectations, and which option may be right for you.
Understanding Traditional Knee Replacement
Traditional knee replacement surgery has been performed for decades and is still highly successful today. The procedure involves removing damaged bone and cartilage from the knee and replacing them with artificial components made of metal, ceramic, or plastic.
During the surgery, the orthopedic surgeon relies on experience, visual assessment, and manual instruments to cut bone, position implants, and align the joint.
Advantages of Traditional Knee Replacement
Even though robotic assistance is growing in popularity, traditional knee replacement continues to offer several benefits:
Long history of proven success
Broad surgeon familiarity and expertise
Effective pain relief and mobility restoration
Suitable for most arthritis cases
Availability in most hospitals
Traditional knee replacement is also generally less expensive than robotic surgery and may be more accessible in smaller cities or healthcare centers that do not yet use robotic systems.
Limitations of Traditional Knee Replacement
However, manual surgery does come with some challenges:
Joint alignment relies heavily on surgeon’s skill
Higher potential for minor variations in implant positioning
Longer recovery in some cases
Slightly higher risk of soft-tissue disruption
Although traditional surgery is extremely safe and successful overall, these factors have inspired the development of more advanced technologies to increase precision and reduce variation.
What is Robotic Knee Replacement?
Robotic knee replacement integrates computer-assisted planning and robotic arm guidance into the surgical procedure.
It doesn’t replace the surgeon—instead, it assists them.
Before surgery, 3D imaging and digital mapping are used to create a personalized model of the patient’s knee. During the operation, the robotic system helps guide the surgeon’s movements to ensure accurate cuts and implant positioning.
This allows the surgeon to execute the procedure with millimeter-level precision.
Advantages of Robotic Knee Replacement
Robotic techniques offer several compelling benefits:
Precise bone cutting and implant alignment
Improved preservation of surrounding tissue
Reduced post-surgery pain and swelling
Smaller incisions and potentially faster recovery
More natural knee feel due to personalized planning
Lower risk of premature implant wear
The technology is especially beneficial for younger and more active patients who want optimal joint performance and longevity.
Limitations of Robotic Knee Replacement
Despite its advantages, robotic surgery also has limitations:
Higher cost compared to manual replacement
Not every hospital offers robotic systems
Learning curve for surgeons new to the technology
Not always necessary for simple cases
While these systems enhance accuracy, outcomes are still strongly influenced by surgeon expertise and proper patient selection.
Comparison: Robotic vs Traditional
To help clarify the differences, here’s a direct comparison:
Factor | Traditional Knee Replacement | Robotic Knee Replacement |
Implant Alignment | Surgeon’s manual judgment | Computer-guided precision |
Soft Tissue Handling | More manual | Higher preservation |
Recovery Speed | Moderate | Often faster |
Minimally Invasive | Sometimes | Typically yes |
Personalization | Standard sizing | Custom or highly precise |
Pain & Swelling | Moderate | Often reduced |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Implant Lifespan | 15–20+ years | Potentially longer |
Recovery Differences: What Patients Can Expect
One of the biggest questions patients ask is how recovery differs between the two methods.
Traditional recovery includes:
Higher postoperative discomfort
Larger incision in some cases
Longer rehabilitation
Slower return to daily activities
Robotic recovery, on the other hand, may offer:
Faster mobility in early stages
Reduced pain and swelling
Lower need for narcotic pain medication
Increased confidence due to better joint stability
However, individual recovery varies based on age, pre-surgery fitness, surgeon experience, and rehab engagement.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Each Type of Surgery?
Ideal Candidates for Traditional Knee Replacement
Patients with advanced arthritis
Elderly patients or lower-activity lifestyles
Individuals prioritizing affordability
Cases with limited access to robotic systems
Ideal Candidates for Robotic Knee Replacement
Younger or active adults
Patients wanting maximum precision
Complex knee deformities
Those seeking faster recovery and natural movement
Tech-assisted customization
Ultimately, the decision should be based on medical evaluation, patient goals, and hospital or surgeon capabilities.
Cost Comparison
Cost remains an important factor. Traditional knee replacement is typically more affordable due to simpler equipment and widespread availability.
Robotic knee replacement is generally costlier because of:
advanced robotic systems
customization
preoperative imaging
Insurance coverage also varies. For many patients, long-term durability and reduced revision risk may offset higher upfront costs.
Surgeon Expertise Matters Most
A key point often overlooked in comparisons is this:
Technology enhances, but does not replace, surgeon skill.
A highly trained surgeon using traditional methods may provide better outcomes than an inexperienced surgeon using robotics.
When choosing between the two:
check surgeon experience
ask about patient success rates
understand available technology
A personalized consultation is the best way to determine the most suitable option.
Which Option Should You Choose?
There is no single best solution for all patients. Both methods are effective and reliable. The choice depends on:
patient lifestyle
age and health
budget
implant expectations
surgeon recommendation
Patients seeking traditional replacement benefit from reliability and accessibility.
Patients seeking robotic replacement benefit from precision, personalization, and recovery advantages.
Many surgeons today combine both approaches depending on patient needs.
The Future of Knee Replacement
Robotic technology is likely to continue evolving.
The future may include:
AI-driven planning
smart implants with real-time feedback
augmented reality surgical visualization
regenerative cartilage solutions
Traditional surgery will remain relevant, but robotics will increasingly play a central role—especially for demanding or complex cases.
FAQs
1. Is robotic knee replacement safer than traditional surgery?
Both robotic and traditional methods are safe, but robotic knee replacement offers enhanced precision and tissue preservation. This can potentially reduce postoperative pain, minimize blood loss, and support smoother recovery. However, safety ultimately depends on the surgeon’s expertise and proper patient selection.
2. Does robotic knee replacement last longer?
While both procedures use durable implants, robotic placement may improve alignment and reduce wear, helping implants function longer. Long-term data is still emerging, but early studies suggest a potential lifespan advantage with robotics.
3. Is robotic knee surgery more expensive?
Yes. Robotic knee replacement generally costs more due to advanced equipment and imaging. However, benefits like better alignment, personalized planning, and lower risk of revision may justify the investment for many patients.
4. Who is a good candidate for robotic knee replacement?
Patients who are younger, more active, have complex knee deformities, or want a quicker return to daily activities may benefit from robotics. That said, traditional knee replacement remains an excellent option for many arthritis cases.
5. How long is recovery after robotic vs traditional surgery?
Traditional recovery may take several weeks to months, depending on age and health. Robotic surgery often enables faster early recovery, less swelling, and quicker mobility—but rehabilitation is still essential in both cases.
6. Is robotic knee replacement available everywhere?
Not yet. Robotics requires specialized systems and trained surgeons, making it more common in advanced orthopedic centers rather than all hospitals. Traditional knee replacement is widely available and still preferred in many locations.
7. Which option is better overall?
There is no universal winner. Both are effective. Robotic surgery enhances precision and customization, while traditional surgery offers reliability and affordability. The best choice depends on your anatomy, lifestyle, and surgeon recommendation.
Final Thoughts
Knee replacement—whether robotic or traditional—remains one of the most transformative orthopedic procedures available. Both methods can significantly improve quality of life, restore mobility, and reduce pain.
Traditional knee replacement provides reliable, proven results and widespread accessibility.
Robotic knee replacement offers enhanced precision, improved soft tissue preservation, and potentially faster recovery.
Rather than asking which method is universally better, the real question is:
Which approach is best for you?
A thoughtful discussion with an experienced orthopedic surgeon, along with personalized evaluation, remains the most effective way to make a confident decision.
